Features
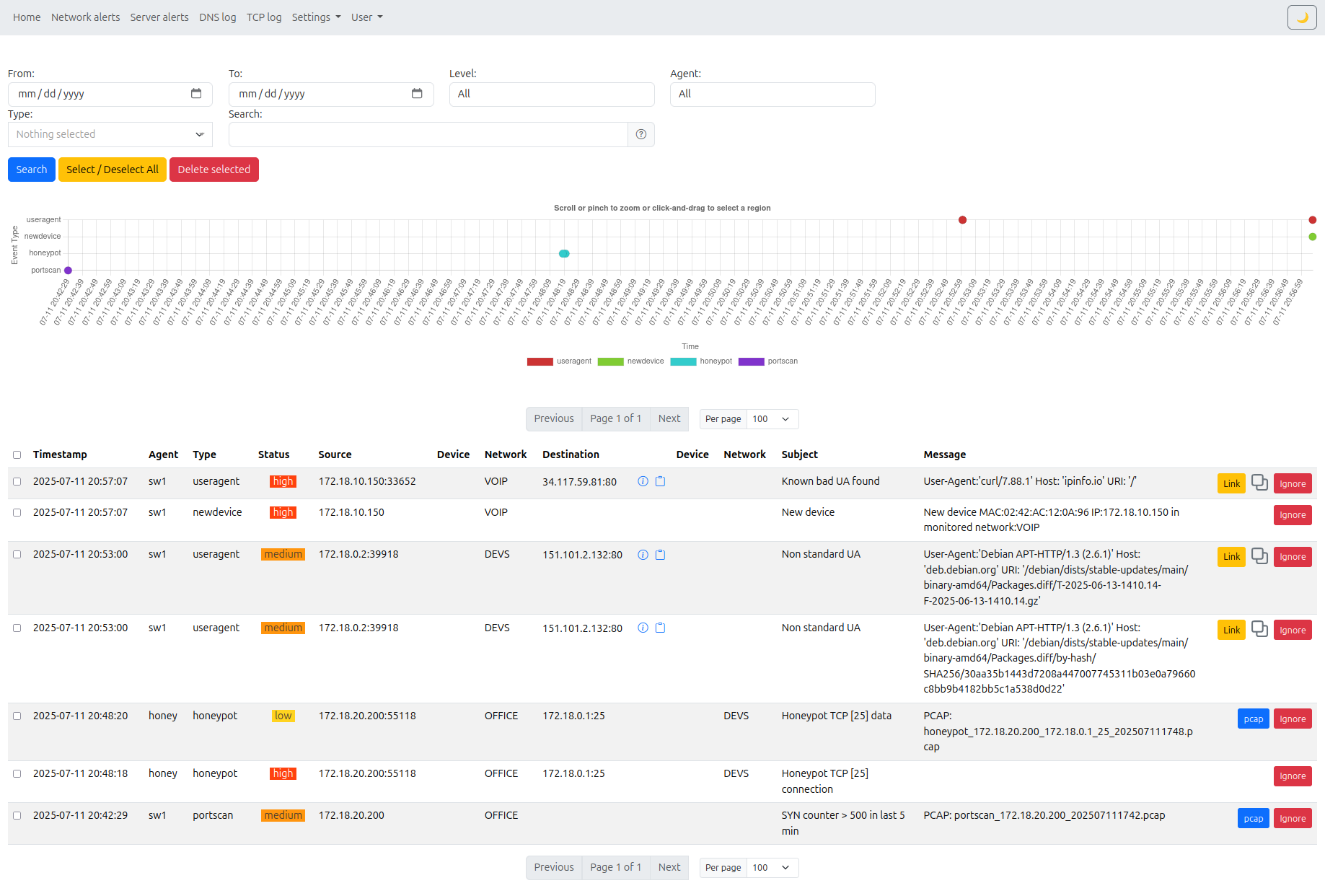
Detection coverage
Reconnaissance and discovery
- Port scanning (single target / multi-target patterns)
- ARP scanning
- DNS scanning patterns (dictionary, PTR)
Lateral movement and segmentation violations
- Unauthorized traffic between network segments
- Workstation-to-workstation and server-to-workstation movement on defined ports
- LDAP-based Active Directory mapping activity anomalies
Unauthorized outbound and policy violations
- Unauthorized outbound traffic from servers with granular IP / ASN / DNS allowlist policy (any or all filters can be combined), generating alerts for traffic outside the defined policy
- SMB traffic directed to the Internet
- TOR traffic detection
Threat intelligence and known-bad matching
- MISP integration for IOC-driven detection
- Known malicious DNS names / IPs / device names
Credential and service abuse
- Password spraying / brute-force behavior patterns
- Suspicious or known-bad HTTP User-Agent values
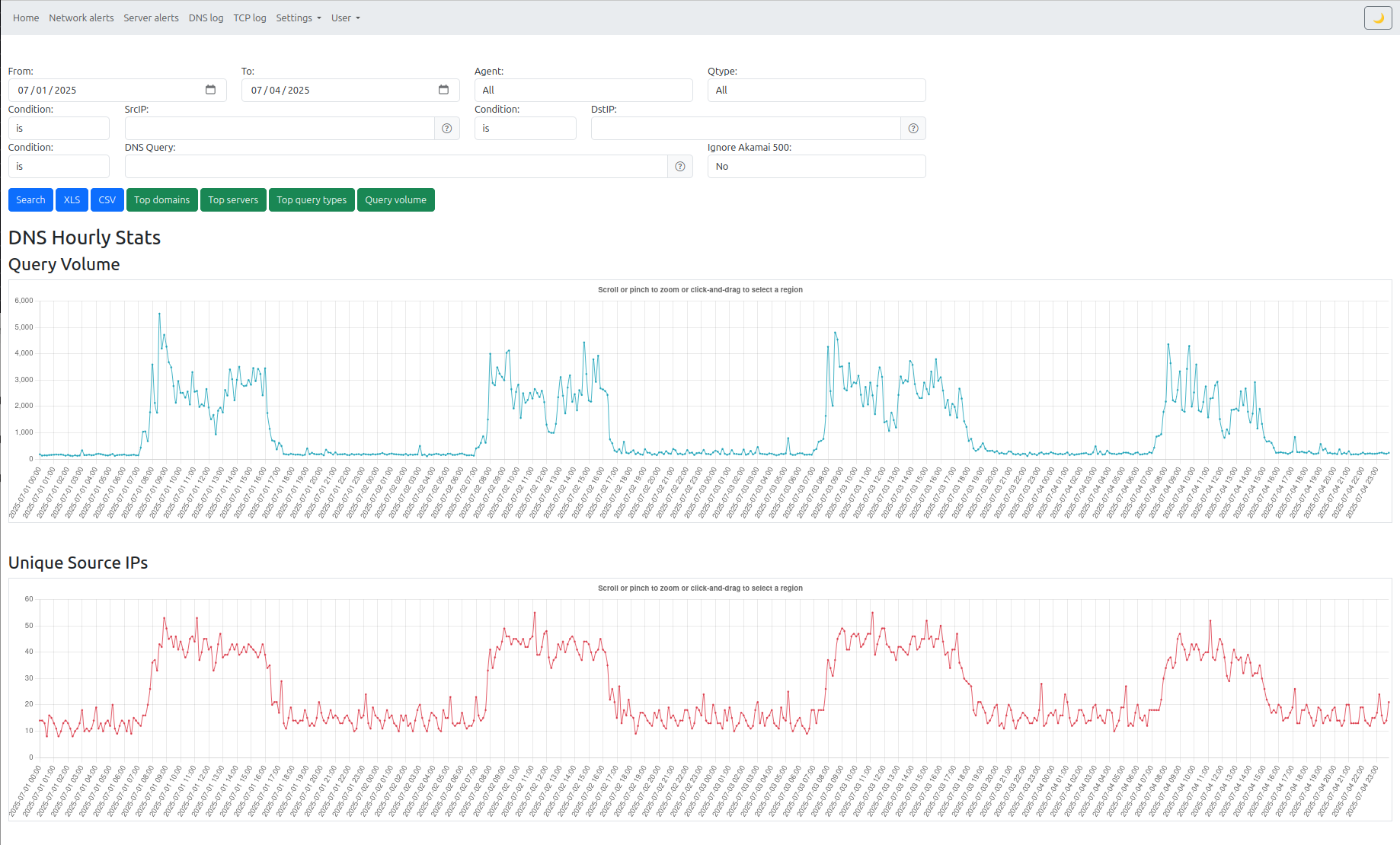
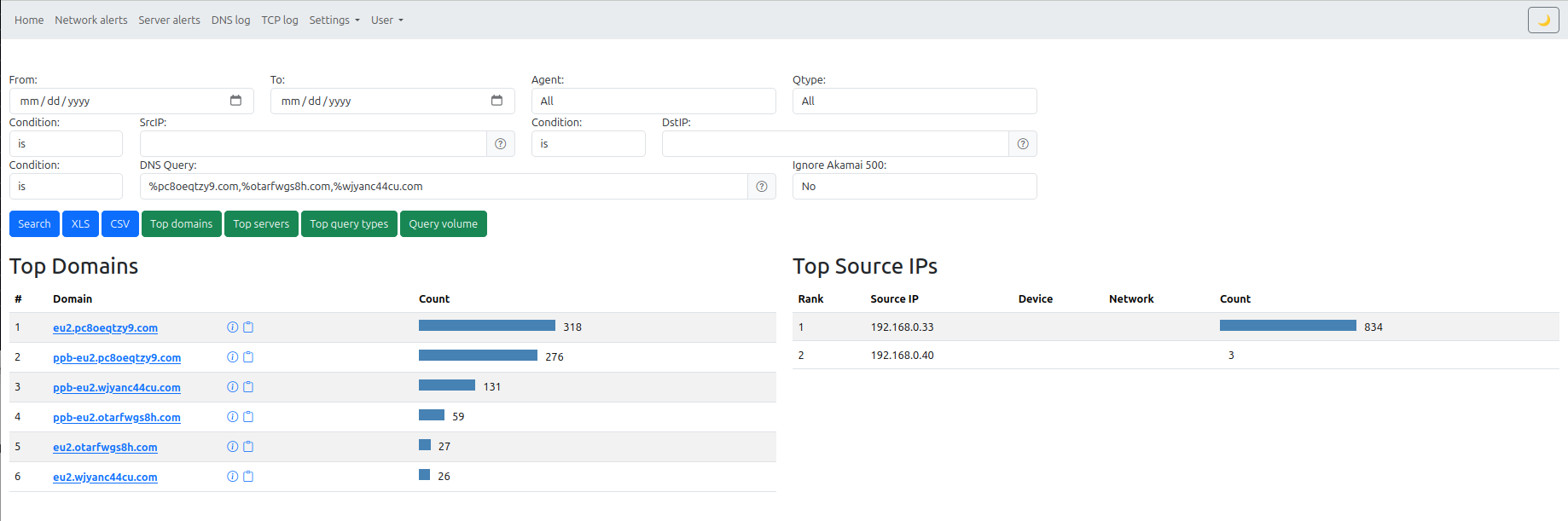
DNS and DHCP security analytics
- DNS C2 behavior
- DGA-like domain detection
- Rogue DHCP servers and DHCP misuse anomalies
Asset and service conformance checks
- Unauthorized network devices
- Unauthorized TCP/UDP services
- Unauthorized DNS server usage
- Unauthorized DHCP server usage
- Passive service discovery view for observed TCP/UDP services across the network
- Service inventory helps admins validate what is actually running, not only what is allowlisted
- New device detection and alerting per network segment
- Device inventory view with IP, MAC, vendor, hostname, first seen, and last seen
- Exportable discovered device inventory
Metadata retained for investigations
Intrudect stores detailed metadata for incident response and retrospective analysis:
- DNS queries
- TCP connections (enriched with PTR and ASN), including received/transferred bytes, packets, and session duration
- DHCP requests
- HTTP requests
- Optional PCAP snippets attached to qualifying alerts
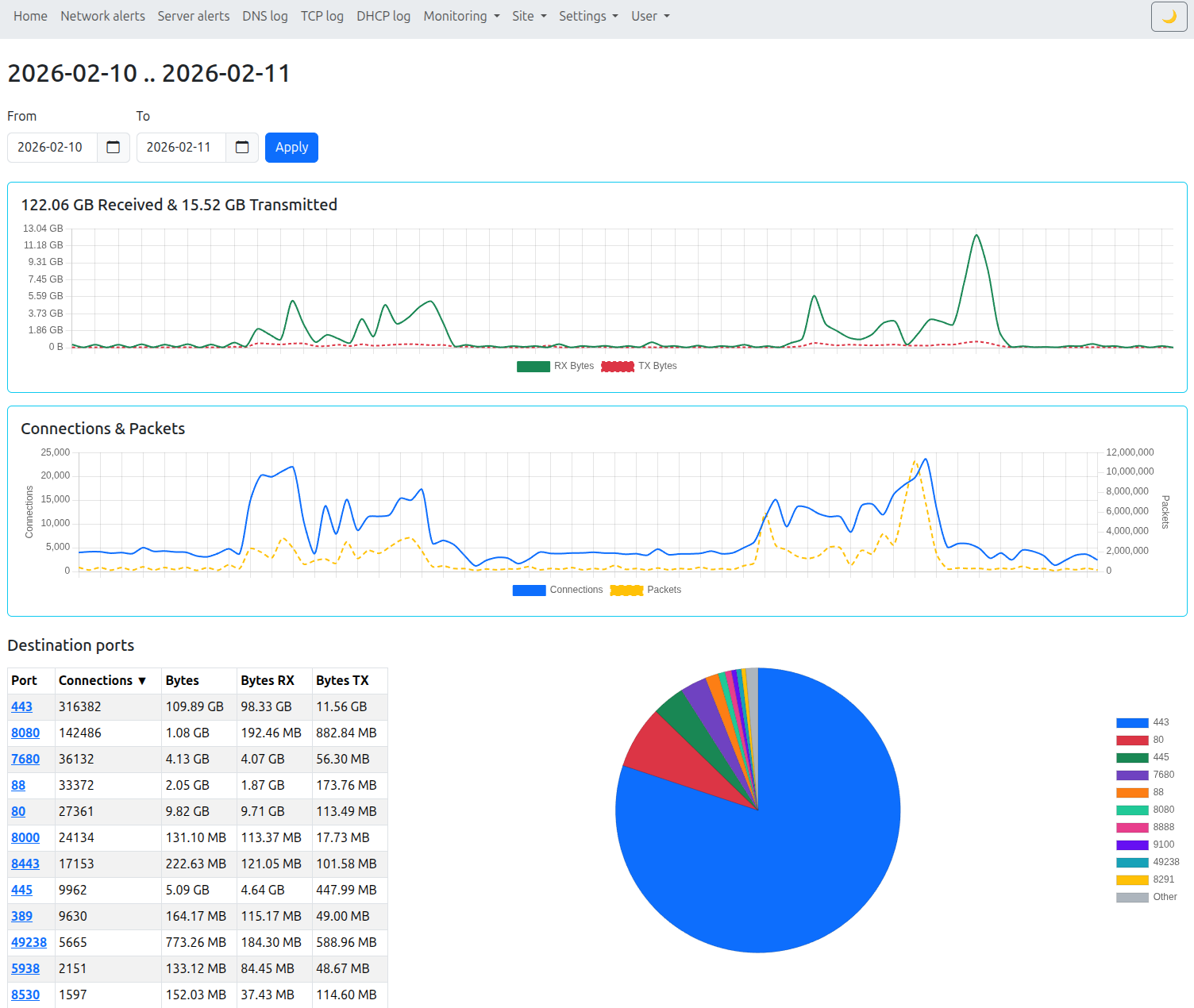
Analysis and visibility
- Search and graph views for connection and DNS behavior
- Country/ASN traffic context for external communications
- Alert context enrichment to speed triage
Operations and governance
- User management with granular permissions (what users can view and modify)
- Audit trail of user actions
- Agent health monitoring and alerts when an agent has not checked in or stops sending metadata
Deployment usage fit
- Works for direct customer deployments and reseller-operated SaaS environments
- Supports multi-site setups where each site needs separate scope and management